Rational Design of New Polymeric Dielectrics |
Rational design of new polymeric materials with attractive properties (high dielectric constant, high breakdown strength, low loss, high glass transition temperature, etc.) is needed to surpass the properties of BOPP in the application of high energy density capacitors and for harsh condition electrifications. Sponsored by the Office of Naval Research (ONR) through Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative (MURI) and other integrated programs, extensive research has been conducted to achieve the design objectives through state-of-the-art “scale-bridging” computations, synthesis, processing, and electrical characterization, and through the creation of a relational database. Link to MURI website
Some recent works can be found in publications at PNAS (DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2115367118), Energy & Environmental Science (DOI: 10.1039/D1EE02630E), Advanced Materials DOI: 10.1002/adma.202000499), Matter (DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2022.06.064), ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, Chemistry of Materials, etc.
Nanostructured Dielectric Materials |
Various Nanostructured dielectric materials have been developed and are under further optimization for thin film, bulk insulation and electric machine insulations. Generally, layered 2D nanocoatings are fabricated via self-co-assembly, spray-coating and in-situ forming methods to offer combined effects of charge blocking and anisotropic energy dissipation. Specifically, an ONR funded program is targeting the the development and performance evaluation of a revolutionary nanostructured insulation in the manufacturing of large propulsion motors with game-changing torque density and payload efficiency for marine Next Generation Integrated Power System.
Recent publications include papers at Advanced Materials (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202101374), iScience (DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104601), Chemical Engineering Journal ( DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.135430), ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.1c14587), Advanced Science, IEEE Access (DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3047103), etc.
Plasma Arc Surface Interaction, EHD & MHD Computations,Instability and Pattern Formation |


Thermal Plasma & Multiphysics Modelling
Thermal plasmas are widely used in a lot of applications and the understanding or some improvement of the corresponding processes, and the modelling of the plasma is becoming a hotspot in recent years. Here a secondary development is applied to reinforce ANSYS Fluent to have the capability of multiphysics coupling to analyze the complicated multiphysics system such as thermal plasmas. In this application, flow dynamics, heat transfer, species transport and EM field are coupled together, and subroutines are under development to predict the behavior of the thermal plasmas and the effect of external factors. The modeling work will be supplemented with experimentally determined data on gas temperature and breakdown strength for gas outflow control and optimization.
Recent publications: JAP (DOI: 10.1063/1.5090867), J Physics D (DOI: 10.1088/1361-6463/abc64b), AIP Advances ( DOI: 10.1063/5.0012159)
|
|
|
The phenomena of an arc hopping along the electrodes have been invariably observed in the Jacob’s Ladder. The major reason lies in the nonlinear plasma sheath. Due to Debye shielding, the space charge in plasma will assembly on the boundary wall/electrode which forms a charge layer, namely the sheath. Due to this charge layer, there will be a potential drop across the plasma-solid interface. The magnitude of this potential drop is susceptible to the charge flux which gives rise to the negative differential resistance (NDR). The NDR is responsible for the observed hopping dynamics, as well as the surface pattern formation on the electrodes. This idea have been numerically demonstrated that the MHD based simulation model, incorporating the NDR featured sheath layer, does capture the hopping pattern of a travelling arc along the Jacob’s Ladder as shown in the video. Recent publications: PNAS Nexus (DOI: 10.1093/pnasnexus/pgac129). |
Harsh Condition Electrification |
High-voltage direct current (HVDC) offers efficient non-synchronized bulk electric power transmissions with economic benefits of reduced power loss and enhanced stability, and has been used widely for grid interconnection, renewable integrations and grid decongestions. Free from reactive power loss, HVDC cables become viable solutions for submarine power transmission, off-shore wind power integration, harsh environment electrification and city in-feeds.
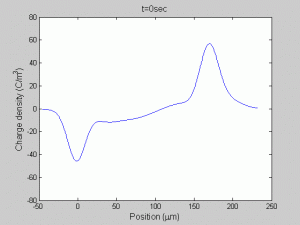
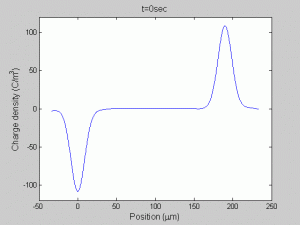
Direct observation of space charge injection and transport in solid dielectrics, as well as their spatial evolution over time, is of great importance in the investigation of design stress and the aging mechanism of engineering dielectrics under high electrical DC field. Through model-aided design, the parallel plate, pulsed-electroacoustic space charge profiling technique is extended to include thermal gradient in thin films. The space charge behavior and dynamics within flat dielectric specimens in the presence of thermal gradient have been studied extensively through the modified pulsed-electroacoustic system to provide insights into the high-field aging mechanisms of new materials developed for energy efficient power devices and renewable integration.
Recent publications: IEEE Electrical Insulation Magazine (DOI: 10.1109/MEI.2019.8804331), Journal of Applied Physics, (https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0091930), Composites Science and Technology, (DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.109241), Journal of Physics D: (DOI: 10.1088/1361- 6463/ac2277)
IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, Vol.37, pp.3733-3736, 2022. DOI: 10.1109/TPEL.2021.3123462
Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 119, 032903, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0050456
Electroactive Materials/Device |

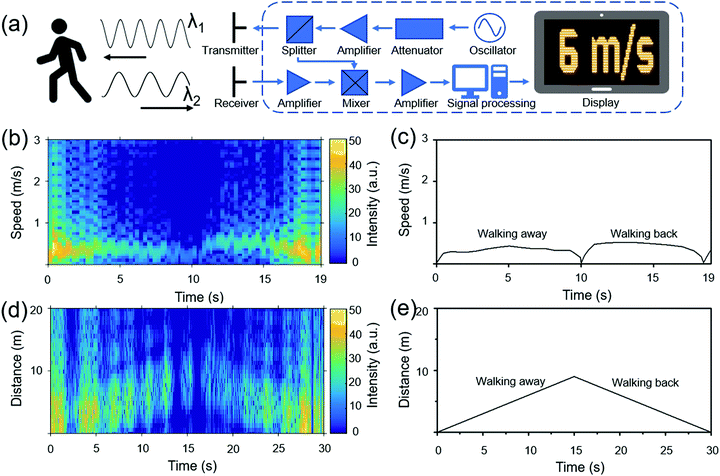
ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c12185
Small https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202103161 Cover Highlight https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/smll.202170170
Advanced Materials Technologies, Vol.7, 2100548, 2022. DOI: 10.1002/admt.202100548
JMCC https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TC00691B Cover Highlight https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/tc/d0tc90089c
Underground Power Distribution |
-
EPR Cables
Shielded distribution cable is employed over the range from a few thousand volts (kV) to about 69 kV to distribute electric power on a local basis in urban and suburban areas without the use of overhead wires. The key element of such cable is the electrical insulation which supports the very high voltage between the conductor and the grounded shield which assures that the electric field remains within the cable. Two insulation technologies compete in the market; insulation based on mineral filled ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) and insulation based on relatively pure cross linked polyethylene (XLPE or TR-XLPE).
-
Frequency Accelerated Aging